Everything You Need to Know About Afrikaans
Even if you’ve never heard about Afrikaans, you might have guessed that it’s a South African language. However, as with most languages, there’s much more to Afrikaans than meets the eye.
Afrikaans was born in Africa from its parent language — Dutch —, but nowadays it’s spoken in places such as Namibia, Botswana, and even in Australia and New Zealand.
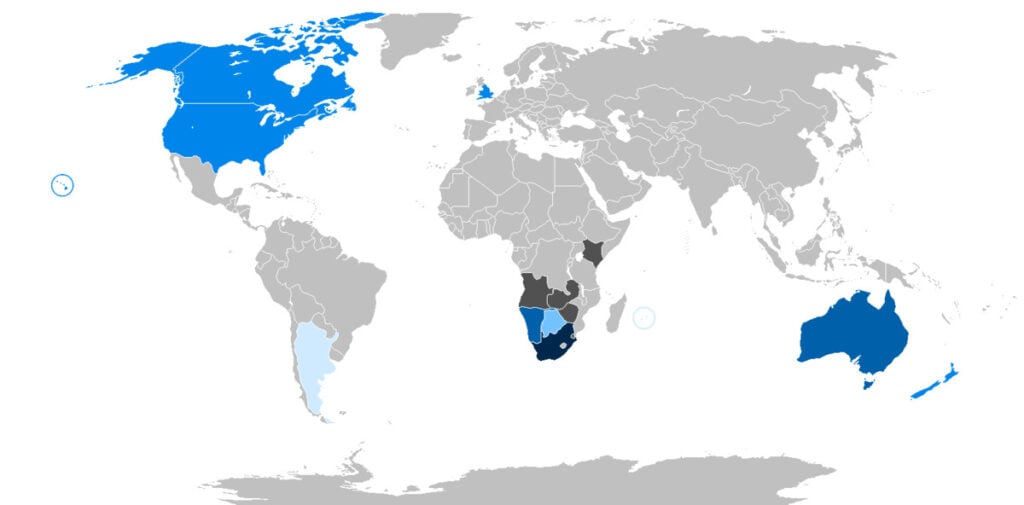
Table of Contents
Map of the number of speakers of Afrikaans across the world via Wikipedia.
This language, which was once pejoratively described as “kitchen Dutch”, has developed into a distinct and fascinating language spoken by almost 18 million people.
Where did the Afrikaans Language Come From?
Brought into South Africa by Dutch settlers in the 17th century, Afrikaans gradually started to develop distinguishing traits in the course of the 18th century. It is the youngest of the West Germanic languages, and one of the last languages in the world to obtain official status.
The Afrikaans language, then, is the offspring of Dutch, once deemed as a mere dialect, then recognized as a language in its own right. Still, being Dutch’s youngest daughter, Afrikaans presents an undeniable resemblance to its parent language, especially in writing. Let’s take a look at a few examples.
English: I love languages.
Dutch: Ik hou van talen
Afrikaans: Ek hou van tale
English: Her hair is blonde
Dutch: Haar haar is blond
Afrikaaans: Haar hare is blond
English: I’m a bit hungry
Dutch: Ik heb een beetje honger
Afrikaans: Ek is ‘n bietjie honger
English: Where do you live?
Dutch: Waar woon je?
Afrikaans: Waar woon jy?
Have you noticed that in some cases it’s harder to spot the differences than to find the similarities? That’s how close these two languages are.
If we want to find major differences between them, we’ll have to analyze their grammar structure and spelling rules. Afrikaans, for example, has more regularity than Dutch, which has more exceptions for every rule.
However, as you can imagine based on the examples above, the similarities between Dutch and Afrikaans are more than enough to make the two languages mutually intelligible. For example, if you find yourself in Namibia and you need directions, you can say “Hoe kan ik naar de luchthaven komen?” (“How can I get to the airport?” in Dutch) and safely expect that Afrikaans speakers will understand.
After all, look at how similar this phrase looks in both languages:
Dutch: Hoe kan ik naar de luchthaven komen?
Afrikaans: Hoe kan ek na die lughawe kom?
A Short History of Afrikaans
So how did the Afrikaans language come of age and gain its current status? For most linguists, Afrikaans was not born as a dialect but as a creole, i.e., as a mother tongue developed from the contact of a European language with a local (usually African) language.
What languages were in the mix? On one hand, Afrikaans used a simplified version of Dutch and added elements of Portuguese and French. On the other hand, indigenous languages such as Khoisan and Bantu, as well as languages spoken by Asian slaves, like Malay, added their own influence.
It is fair to say, then, that the Afrikaans language is a byproduct of colonialism, a simplified form of 17th century Dutch brought into South Africa by Dutch settlers who were forced to communicate with the Indigenous people.
This contact language, which initially elicited snobbish judgments, gained a reputation throughout the 18th century as it started to appear in official newspapers and even in literature. At the same time, Afrikaans was also taught in Muslim schools, becoming a rare historic example of a Germanic language being written in Arabic script.
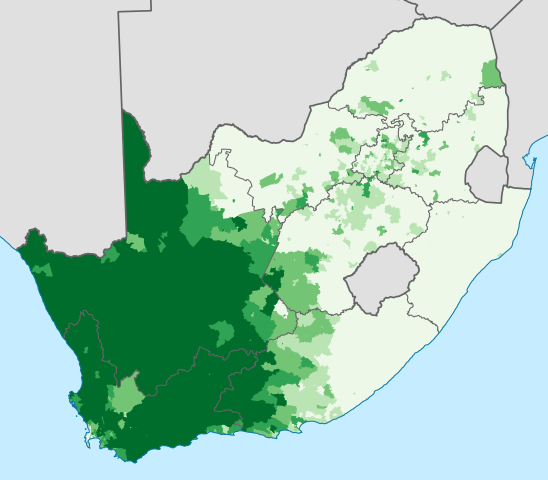
Geographical distribution of Afrikaans in South Africa via Wikipedia.
Nowadays, Afrikaans is considered one of the standard languages both in education and public life in South Africa together with English and nine other languages.
In fact, its status as a standalone language is so solid that it has its own local varieties, among them a secret prison dialect that is a mix of elements from Afrikaans and Zulu.
However, because Afrikaans has long been highly standardized, these local varieties are all perfectly intelligible and not particularly different from one another.
Where Can I Hear Afrikaans Today?
Being an official language spoken natively by about 7 million people, it’s shouldn’t be hard for language-lovers to find people who speak Afrikaans.
In fact, out of all the languages spoken in Africa, Afrikaans is the most geographically dispersed, meaning that you can find Afrikaans speakers almost everywhere you go. In the American movie industry, for example, you can find A-list celebrities like Charlize Theron who speak it fluently.
It’s no wonder, then, that the Afrikaans language has made it into Hollywood and that, nowadays, you can find many movies on Netflix which are totally or partially spoken in Afrikaans. (The short film Baxu and the Giants is our top recommendation!)
Are you thinking about learning Afrikaans? Then you might want to check our online courses taught by native Afrikaans tutors. No matter what your current level is, they will make sure that you get a personalized learning experience specially designed to suit your needs and preferences. Reach out to us now and we’ll get back to you right away so you can start immersing yourself in this wonderful language as soon as possible.



